
Step to step tutorial to MongoDB for beginners
MongoDB is a NoSQL (non-relational) database. There are several types of NoSQL databases, and MongoDB is a document-based NoSQL database that is open source . This MongoDB lesson is meant for beginners, so even if you have no prior understanding of the database, you will be able to grasp it.
In this blog, you will learn what MongoDB for beginners
What exactly is MongoDB?
MongoDB is an open-source database with a document-oriented data format and a non-structured query language, according to its description. It is one of the most powerful NoSQL databases and systems available today.
MongoDB Atlas is a globally accessible cloud database solution for modern applications. This best-in-class automation and well-established processes enable completely managed MongoDB deployments on AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure.
It also guarantees availability, scalability, and adherence to the most severe data security and privacy standards. MongoDB Cloud is a unified data platform that comprises a global cloud database, search, data lake, mobile, and application services, as well as a global cloud database.
Because it is a NoSQL tool, it does not employ the traditional rows and columns associated with relational database administration. It is a collection-based and document-based architecture. A collection of key-value pairs is the basic unit of data in this database. It provides for varied fields and formats in documents. This database stores documents in the BSON format, which is a binary version of JSON.
MongoDB is a highly elastic data model that allows you to aggregate and store data of multiple kinds without sacrificing strong indexing options, data access, or validation criteria. When you wish to change the schemas dynamically, there is no downtime. What this implies is that instead of spending extra time preparing data for the database, you can focus on making your data work harder.
MongoDB's for beginners architecture
Database: A database may be thought of as a physical container for data. With many databases running on a single MongoDB server, each database has its own set of files on the file system.
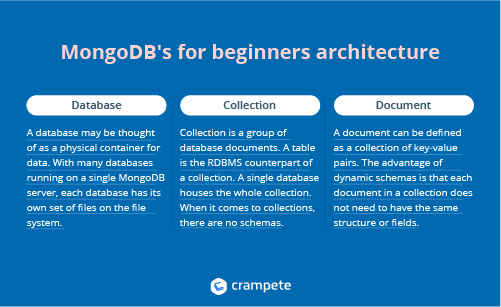
Collection: The term "collection" refers to a group of database documents. A table is the RDBMS counterpart of a collection. A single database houses the whole collection. When it comes to collections, there are no schemas. Different documents within a collection may have different fields, but most papers within a collection are intended for the same purpose or to achieve the same end objective.
Document: A document can be defined as a collection of key-value pairs. Dynamic schemas are linked to documents. The advantage of dynamic schemas is that each document in a collection does not need to have the same structure or fields. In addition, the common fields in a collection document might include a variety of data types.
How to use MongoDB for beginners
Step 1) Download MongoDB Community Server from this URL. For Windows, we'll use the 64-bit version.
Step 2) After the download is complete, double-click the msi file to run it. In the start-up screen, select Next.
Step 3) Click Next after accepting the End-User License Agreement.
Step 4) To install all of the components, click the "complete" button.
Step 5) “Run service as Network Service user” should be selected. Note the location of the data directory; we'll need it later.
Next should be selected.
Step 6) To begin the installation, click the Install button.
Step 7) The installation process begins. Once you've finished, click Next.
Step 8) To finalise the installation, click the Finish button.
MongoDB's Most Important Features
Documents
Data is stored in MongoDB as JSON documents.
The document data model corresponds to objects in application code in a natural way, making it simple to understand and use for developers.
A JSON document's fields might differ from one to the next. When compared to a typical relational database table, where adding a field means adding a column to the database table itself, and therefore to every record in the database, adding a field implies adding a column to every record in the database.
To describe hierarchical connections and to hold structures such as arrays, documents can be nested.
The document format gives you the freedom to work with messy, complicated data from a variety of sources. It allows developers to easily add new features to their applications.
MongoDB transforms documents into a Binary JSON or BSON format for internal access and to accommodate more data types. MongoDB, on the other hand, is a JSON database from the developer's perspective.
Collections
A collection in MongoDB is a set of documents.
You can think of a collection as a table if you're familiar with relational databases. MongoDB collections, on the other hand, are considerably more adaptable. Documents in the same collection might have various fields since collections don't impose a schema.
Each collection corresponds to a single MongoDB database. Use the listCollections command to see which collections exist in a database.
Replica sets
Keeping several copies of your data is a key approach to achieve high availability. High availability is integrated into the design of MongoDB.
When you establish a database in MongoDB, the system produces at least two more copies of the data, which is known as a replica set. A replica set is a collection of at least three MongoDB instances that constantly duplicate data amongst themselves, providing redundancy and protection against downtime in the event of a system breakdown or scheduled maintenance.

Sharding
A contemporary data platform must be capable of handling extremely rapid queries and large datasets with ever-larger clusters of tiny devices. Sharding is a phrase for intelligently spreading data over many computers.
In MongoDB, how does sharding work? MongoDB distributes documents in a collection among the shards of a cluster by sharding data at the collection level. As a consequence, a scale-out architecture that can handle even the most demanding applications has been created.
Indexes
The efficient execution of queries is aided by indexes. MongoDB has a number of indexing methods available, including compound indexes on multiple fields. Indexes, which are properly chosen, speed up queries by scanning the index rather than reading every page in the collection.
There is more work to be done in determining which queries might benefit from indexing. Performance Advisor is one tool that conducts this analysis for you. It analyses queries and proposes indexes that might enhance query performance.
Aggregation Pipelines
Aggregation pipelines are a versatile framework for constructing data processing pipelines in MongoDB. It has hundreds of steps and over 150 operators and expressions, allowing you to process, manipulate, and analyse data at scale. The Union step, which flexibly aggregates findings from different collections, is a recent feature.
Explore mongodb course from here
Comparison between MongoDB for beginners and other Databases
MongoDB vs RDBMS:
You may directly compare MongoDB NoSQL to RDBMS and map the two systems' different terminologies: The table join is an embedded document, the column is a field, the tuple/row is a document, and the RDBMS table is a MongoDB collection.
The number of tables and the relationships between them are shown in a conventional relational database structure, however MongoDB does not use the idea of relationships.
Examine the table below to see how a professional NoSQL database like MongoDB differs from a relational database management system.
Important MongoDB Features
Queries: Ad-hoc and document-based searches are also supported.
Support for indexing: Any field in the document may be indexed.
Replication: It allows for Master-Slave replication. MongoDB keeps multiple copies of data using native apps. One of the replica set's benefits is that it contains a self-healing shard, which helps to prevent database downtime.
Multiple Servers: The database can be spread over several servers. Data is replicated to ensure that the system is unbreakable in the event of hardware failure.
Auto-shading: Auto-sharding is a technique for distributing data over numerous physical divisions known as shards. MongoDB's automated load balancing functionality is due to its sharding.
MapReduce: It supports MapReduce as well as configurable aggregation techniques.
Schema-less Database: It's a C++-based schema-less database.
Document - oriented storage: It employs the BSON format, which is a JSON-like format, for document-oriented storage.
Procedures: MongoDB JavaScript works well as the database uses the language instead of procedures.
What are the benefits of MongoDB technology?
This method solved one of the most serious flaws in traditional database systems: scalability. Businesses' database systems have to be updated to keep up with their ever-changing demands. MongoDB is incredibly scalable.
It makes data retrieval simple and allows for continuous and automated integration. There are a variety of reasons why you should use MongoDB in addition to these advantages:
- No downtime while the application is being scaled
- Performs in-memory processing
- Text search
- Graph processing
- Global replication
- Economical
Furthermore, organisations are rapidly discovering that MongoDB checks all the boxes when it comes to satisfying their needs. Here's how to do it:
- MongoDB is the ideal combination of technology and data for gaining a competitive advantage.
- Because it significantly minimizes hazards, it is best suited for mission-critical applications.
- It decreased the total cost of ownership and expedited the time to value (TTV).
- It creates applications that standard relational databases just cannot.
Advantages of MongoDB project for beginners
You should understand why MongoDB is considered one of the greatest NoSQL databases by technocrats.
Learn about the six characteristics of MongoDB that can help you reap its benefits:
1. Platform for Distributed Data
- MongoDB may be operated across globally dispersed data centres and cloud regions, enabling unprecedented levels of availability and scalability.
- MongoDB scales elastically in terms of data volume and performance with minimal downtime and without requiring changes to your application.
- The technology allows you to have adequate flexibility while maintaining consistency across several data centres.
2. Iterative and rapid development
- Changing business needs will no longer have an impact on your company's project delivery performance.
- Developers can quickly construct and grow applications thanks to a flexible data format with changeable schema and powerful GUI and command-line tools.
- Continuous integration and delivery for productive operations are made possible by automated provisioning.
- RDBMS complicated procedures and static relational structures are now a thing of the past.

3. Data Model Flexibility
- Data is stored in MongoDB as flexible JSON-like documents, making data persistence and combining simple.
- The document model is mapped to the objects in your application code, making data manipulation simple.
- Schema governance restrictions, data access, sophisticated aggregations, and extensive indexing features, of course, are all unaffected.
- Dynamically changing the schema is possible without any downtime.
- Due to this flexibility, a developer needs to worry less about data manipulation.
4. Lower TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
- When MongoDB is utilised, application developers can perform a much better job.
- Thanks to the Atlas Cloud service, the operations staff can also do a good job.
- Because MongoDB operates on commodity hardware, costs are considerably reduced.
- With annual subscriptions, the technology provides on-demand, pay-as-you-go pricing as well as 24/7 global support.
5. Integrated Feature Set
Because of analytics and data visualisation, event-driven streaming data pipelines, text and geographic search, graph processing, and in-memory performance, a wide range of real-time applications are available.
Additional sophisticated technologies, as well as distinct integration needs, are required for RDBMS to do this.
6. Commitment to the Long Term
- You'd be astounded to learn of this technology's evolution.
- It has received more than 30 million downloads, 4,900 customers, and 1,000 partners.
- If you incorporate this technology into your company, you can be assured that your money is well spent.
For obvious reasons, MongoDB does not support the SQL language. Because MongoDB is a document-based query language that may be as useful as SQL, its querying approach is dynamic on documents. MongoDB is simple to scale, and no conversion or mapping of application objects to database objects is required. It uses internal memory to provide quicker data access and to store the working set.
Where may the MongoDB NoSQL database be used?
MongoDB is a NoSQL database that may be used extensively in Big Data and Hadoop applications to cope with massive volumes of NoSQL data, which makes up a large part of Big Data. MongoDB and SQL are both database systems, however their efficiency in today's environment distinguishes them.
MongoDB may also be used to parse any unstructured streaming information in social media and mobile applications. The MongoDB NoSQL database is also widely used in content management and distribution. User data management and data hubs are two further fields.
Who makes use of MongoDB?
MongoDB is a database service for apps or data storage systems that is utilised by a large number of IT companies today. Over 4000 organisations have confirmed that they utilise MongoDB as a database, according to a survey done on MongoDB. Some of the companies that use MongoDB include the ones listed below.
- IBMUber.
- Lyft.
- Intercom
- Citrix
- Delivery Hero.
- InVision
- HTC
- T-Mobile
- LaunchDarkly.
- Sony
- Stack.
- Castlight Health
- Accenture
- Zendesk
MongoDB's Use Cases
Single view:
- Even on a shoestring budget, MongoDB can rapidly and simply construct a single view of anything.
- To give a single perspective of anything, a single view application gathers data from several sources and saves it in a central repository.
- With its document model, Dynamic Schemas, and expressive query language, MongoDB makes single views simple.
- Financial services, government, high-tech, and retail all employ MongoDB's single view.
Internet of Things:
- MongoDB can help you get the most out of the Internet of Things as fast as possible.
- MongoDB supports high-speed data ingestion as well as real-time analytics, which is useful for IoT. MongoDB is used by companies like Bosch and Thermofisher for IoT.
Real-time analytics:
- With MongoDB, you can analyse any data quicker, anywhere, and in real time.
- It can store any sort of data, regardless of its structure, format, or source, or how often it changes.
- MongoDB is designed to run on commodity hardware in your data centre or in the cloud, with no extra hardware or software required.
- MongoDB can analyse data of any structure in the database, delivering real-time results without the need for expensive data warehouse loads.
Payments:
- Payment platforms must deliver a flexible, real-time, and improved customer experience to surpass the competition.
- From consumer brands to companies, industry leaders utilise MongoDB as the backbone of their always-on, always secure, always available payments infrastructure.
- MongoDB's payment services are used by companies like nets icon solution.
Gaming:
- Data has always been a big part of video games. Data is required to improve the performance of games.
- It helps with everything from player profiles to telemetry to scoreboard matching.
- MongoDB's flexible document data structure makes it simple to assess a player's capacity.
- Add features like achievements, progression-based unlocks, in-game money, new equip classes, and more to player profile items.
- Use enterprise-grade security features at the data layer to keep your gamers secure.
- MongoDB is used in gaming by companies like Sega and Faceit.
MongoDB Syllabus for beginners
- Introduction
- Database,collection & document
- Data types & querying
- Services
- MongoDB with PHP
- MongoDB with Nodejs
Knowing several frameworks will help you advance in your Big Data profession. MongoDB certification will help you improve your abilities as a Big Data Engineer and will also help you advance your career in terms of pay and advancement.
MongoDB is a robust and thorough database management system, and it will take you around three weeks to get up to speed.
Few centres offer MongoDB course fees at a nominal rate or for free.
What is MongoDB NoSQL's scope?
Mongo is being effectively deployed by some of the world's largest organisations, with more than half of the Fortune 100 firms using this amazing NoSQL database system. It has a thriving ecosystem, with over 100 partners and a steady stream of investors putting money into the technology.
MetLife, one of the world's largest insurance firms, uses MongoDB extensively for customer care applications; Craigslist, an online ads search site, uses MongoDB heavily for data preservation. The New York Times, one of the most well-known companies in the media sector, uses MongoDB for photo uploads and the application that is used for form-building.
Finally, the world's top scientific enterprise, sponsored by the CERN physics laboratory, uses MongoDB significantly for data aggregation and data discovery applications, demonstrating the breadth of MongoDB's supremacy.
Who is the best person to teach MongoDB technology to?
- Developers, architects, and administrators of software
- Professionals who work with databases and analytics
- Professionals in the fields of system administration and research
What role will technology play in your professional development?
- According to InfoWorld, MongoDB is the most frequently used NoSQL database.
- In the United States, a MongoDB Database Administrator may earn up to $129,000 per year .
- Within the next two years, the Hadoop and NoSQL industries are anticipated to reach $3.3 billion, according to Wikibon.
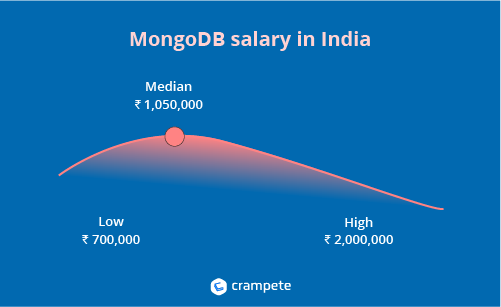
MongoDB salary in India
In India, the average mongodb salary is 1,040,000 rupees per year, or Rs.535 per hour. Starting salaries for entry-level jobs start at 600,000 per year, with most experienced professionals earning up to 2,000,000 per year.
Supporting languages:
Official MongoDB driver support is now available for all common programming languages, including C, C++, C#, Java, Node.js, Perl, PHP, Python, Ruby, Scala, Go, and Erlang.
Custom MongoDB Setup Process
- Setting up MongoDB on Mac OS X, and
- Setting up MongoDB on Windows
How to Install Mongo in macOS
It will be much easier to install MongoDB on your Mac than it will be on Windows. We can get the newest version from MacPorts by running a few instructions in the Terminal.
Let's start by making sure MacPorts is up to date. Type the following in Terminal:
sudo port selfupdate
You may also use the debug flag to get more output:
sudo port -d selfupdate
The download and installation procedure might take a few minutes.
Following the completion of this update, we only need to run a single line in the Terminal. The most recent MongoDB library files will be downloaded and stored with other system requirements.
port install mongodb
Even with a fast Internet connection, this process might easily take 10-15 minutes. The installation takes some time and might be done faster, but don't worry about it till you see the flashing terminal command open.
Then you should be able to use the following command to start the server:
Mongod
Finally run these following commands to set up the launcher. You can choose to restart your computer afterwards and see if Mongo works right on reboot.
How to Install Mongo in Windows
Without utilising the Administrator account, I had a lot of trouble getting MongoDB to install and function properly. This isn't necessary because the option to "Run as Administrator" is always accessible.
If you have the ability, you may simply execute this command in the command prompt and restart your computer. The Administrator should appear as a new login option.
net user administrator /active:yes
If you have any problems, MongoDB has a fantastic online installation guide designed specifically for Windows users. To acquire your copy, go to the downloads page and look for your Windows version. MongoDB 2.2.0 is the most recent stable release at the time of writing this article: below are the direct downloads for Win32 and Win64.
We are going to place all these files directly inside a directory C:\mongodb\. So once the download finishes, extract the zip and open the folders until you find /bin/ with a few other files. Select all these and cut/paste into our new C:\mongodb\ directory.
Now still inside this folder alongside \bin\ create a new folder named “log” which will store all the MongoDB system logs. We also need to create two external directories for data storage,
C:\data\ and C:\data\db\.
This is the part where using a non-Administrator account may cause trouble. Open up the command prompt and run cd C:\mongodb\bin.
Then we are looking to start the mongod.exe in shell, but after running this you’ll notice the operation will freeze when listening for connections. Well it’s not actually frozen, we are running Mongo directly through the terminal.
This will get tedious to perform each time, so let's execute a programme to configure Mongo to start as a Windows Service automatically.
> echo logpath=C:\mongodb\log\mongo.log > C:\mongodb\mongod.cfg
The first command will generate a log file as well as the service's settings. As a database administrator, this is not essential, but it is excellent practise.
Now execute these two lines of code in the terminal to create and start the service.
> C:\mongodb\bin\mongod.exe --config C:\mongodb\mongod.cfg --install
> net start MongoDB
If there are no mistakes, the procedure is complete.
Open the Run menu (Windows + R) and type services.msc to see if the service is running.
This displays an active list of services, where you should see MongoDB with the status "active" and the startup type "automatic" if you scroll down.
As on the Mac install you can access the Mongo shell terminal right from the command prompt. Change directories to C:\mongodb\bin\ and type mongo, then hit Enter.
You should be able to access the current MongoDB server straight away. Mongo shell commands may now be used to build databases, collections, save new data, and update existing data entries.
To see all current databases on the server, type the following command:
> show dbs
MongoDB is an extremely helpful NoSQL database that is utilised by some of the world's largest companies. MongoDB provides a never-before-seen collection of functionality to companies in order to parse all of their unstructured data, thanks to some of its most powerful features.
As a result, individuals who are qualified and certified to work with the fundamentals and advanced levels of MongoDB technologies may expect to see their careers take off in a big way. MongoDB for beginners may be utilised for datasets such as social media, videos, and so on because of its adaptability and scalability. Clients and consumers of MongoDB will have no need for other databases.
FAQs
1. What is MongoDB and how it works?
MongoDB is a NoSQL database management system that is free and open source. Traditional relational databases are replaced by NoSQL databases. Working with huge quantities of dispersed data is a breeze with NoSQL databases. MongoDB is a database management system that can store and retrieve document-oriented data.
2. How to use MongoDB step by step?
- Step 1: installation.
- Step 2: starting the MongoDB server
- Step 3: starting the client.
- Step 4: creating a database.
- Step 5: creating a collection.
- Step 6: add documents to a collection.
- Step 7: manage documents.
3. What can I learn in MongoDB?
The fundamentals of MongoDB—connecting to a MongoDB Cluster, MongoDB's document storage model and principles of flexible schema design, the basic architecture of MongoDB clusters, CRUD operations, using MongoDB Compass, etc.
4. Why is MongoDB popular?
MongoDB's document-oriented data model makes it easier to add and update fields, among other things, than any other NoSQL database and significantly more than any relational database. As it were, with MongoDB, form follows function. MongoDB is popular because it is simple to understand and use.
5. What is MongoDB vs MySQL?
MongoDB is a database that was created as an open-source project by MongoDB, Inc. MongoDB saves information in JSON-like documents with a variety of structures. It's a well-known NoSQL database. Oracle Corporation develops, distributes, and supports MySQL, a prominent open-source relational database management system (RDBMS).

Accelerate Your Career with Crampete




