
Eager to become a node js developer?
The next step for front-end developers who have a solid understanding of JavaScript and many frameworks is to study Node.js. This framework opens the door to the backend, allowing you to work as a full-stack developer. Although this isn't the only incentive to learn Node.js.
According to the Stack Overflow Engineers Survey 2021, Node.js is the most popular framework among software developers' various technologies. The reason for this is that Node.js allows you to create a wide range of apps, from real-time conversations to SPAs and IoT solutions. As a result, if you're evaluating which framework to add to your tech stack next, Node.js is worth considering.
We cover all you need to know about Node.js in this post, as well as a Node.js developer roadmap for beginners.
What is node js?
Node.js is a framework for quickly creating fast and scalable network applications based on Chrome's JavaScript engine.Node. js uses an event-driven, non-blocking I/O model that makes it lightweight and efficient,which is ideal for data-intensive real-time applications that run across multiple devices.
What is the purpose of node js?
Node. js enables web development in JavaScript by bringing event-driven programming to web servers. Using a simplified model of event-driven programming that uses callbacks to signal the completion of a task, developers can create scalable servers without using threading.
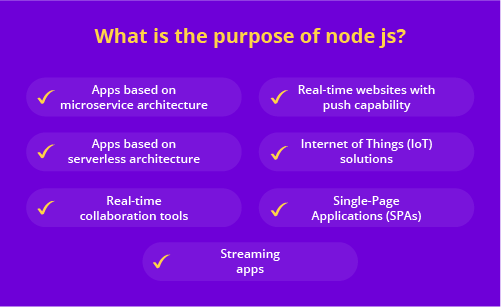
Software developers can use Node.js to create a variety of applications, including:
- Streaming apps
- Apps based on microservice architecture
- Real-time collaboration tools
- Internet of Things (IoT) solutions
- Single-Page Applications (SPAs)
- Apps based on serverless architecture
- Real-time websites with push capability, and others
It is possible due to the non-blocking input-output mechanism and event-driven functionality which makes Node.js an effective and lightweight solution for running data-intensive real-time applications on distributed devices.
The most popular digital companies that use Node.js to build their applications include PayPal, LinkedIn, Netflix, Uber, GoDaddy, NASA, eBay, Walmart, and others.
Node.js Developer duties and responsibilities
- Develop apps and services as part of a team utilising Agile development methodologies.
- Contribute to process and infrastructural improvements for the team and the company.
- Create a user interface for customers as well as back-end services for payment processing administration and management
- Code, teste and operate node.js based services
- Use tools and inventiveness to effectively detect and correct problems before they become an issue.
Node.js Developer requirements and qualifications
- Working experience as a Node.js Developer , Bachelor's degree in computer science or a related area
- Knowledge of Node.js in depth
- Hands-on expertise with HTML, CSS, and AJAX. Object-oriented JavaScript, python, full stack development and SVG design experience.
- Knowledge of web libraries and frameworks like AngularJS, Polymer, and Closure is useful.
- Knowledge of the whole web stack, including protocols and web server optimization methods
- Strong analytical abilities and a proclivity for problem-solving
- Pay close attention to the details.
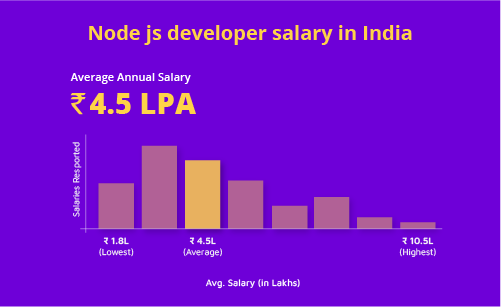
Node js developer salary in India
The average yearly pay for a Node JS Developer in India is 4.5 lakhs, with salaries ranging from 1.8 lakhs to 10.5 lakhs.
In India, the average salary for a full-stack software developer with Node. js skills is Rs.535,000. As a Full Stack Software Developer with less than a year of experience, you can expect to make an average total compensation of Rs.357,800 (which includes tips, bonus, and overtime pay).
Node js development trends
What are the most popular Node.js developer roadmap trends to follow in 2023? Let’s have a look at the most outstanding ones.
Real-Time Applications
Businesses in gaming, e-commerce, social networking, and other industries have embraced real-time apps. These apps operate in real time, providing their users the impression of instant reaction. Real-time apps have a latency of seconds and are used to create online games, videoconferencing applications, instant messaging apps, and other applications. All of these apps demand a lot of processing power on the backend, which Node.js excels at. Learn how to become a back end developer from here.
Stacks of MEAN and MERN
MEAN (MongoDB, Express, Angular, Node.js) and MERN (MongoDB, Express, React.js, Node.js) are strong stacks for creating basic and sophisticated solutions, respectively. The implementation of Angular or React frameworks is the major distinction between the two stacks.
Explore how to become a mean stack web developer by checking out here.
Model-View-Controller development paradigm, two-way data binding, modularization, and other features are all included in Angular. It enables the creation of interactive, dynamic, and contemporary SPAs using clean and simple code.
Get certified in mongodb course from here
React.js is a lightning-fast framework for creating UI’s and its components, as well as Single-Page Applications. It has a virtual DOM and is solely concerned with the view layer. React.js is a lightweight and easy option for rapid web application development because of these qualities.
Get to learn reactjs online course from here
Serverless Architecture
Node.js developers may concentrate on the application's functionality rather than setting servers or worrying about numerous HTTP entry points thanks to serverless design. Cloud computing platforms are in charge of all of this. As a result, software developers may profit from serverless architecture in a variety of ways, including:
- Improved coding quality
- Development time is shorter,
- Development costs are lower.
- Code components that can be reused
- Architecture that is easier to scale
GraphQL
The use of GraphQL instead of RESTful API technology is a feasible option. This API server-side runtime returns the precise data from the databases that the user requested. As a result, this technique looks to be quicker and more versatile than conventional REST.
GraphQL has recently attracted the attention of many developers all around the world. Airbnb, Atlassian, Compara, Coursera, PayPal, Pinterest, and others are among the most well-known GraphQL users. To create apps with well-structured queries and data replies, many software developers integrate their Node.js-based applications with GraphQL technology.
Microservice Architecture
The microservice architecture enables enterprise-level projects to be developed with code that is easy to maintain and adapt. It divides an application's architecture into loosely linked modules that communicate with one another using APIs.
Software developers may use microservice architecture to design programmes in tiny, quick iterations, scale them quickly, and develop them faster. To create microservice architectural solutions, Node.js leverages the Docker containerization technology and Kubernetes Services.
What you need to know to get started with Node.js:
- Knowledge of development techniques such as Agile, DevOps, RAD, Scrum, and others
- Comprehensive understanding of front-end programming languages such as HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScript
- At least one front-end development framework, such as JavaScript, Angular, or Vue.js, is required
- A thorough knowledge of what asynchronous programming is and how it works
- User authentication and authorisation experience across many systems, servers, and settings.
- Knowledge with development tools such as Git, SVN, and CVS is required.
- Integration of several data sources into a single system.
- Good understanding of how to use preprocessors for server-side CSS, such as Stylus
- Having knowledge of error management and unit testing experience.
Click here to learn front end online course
To become a desirable Node.js developer, you'll need to learn the following:
- Examine the js architecture, which is based on a single-threaded event loop paradigm and is event-driven.
- Learn how to use Node Package Manager (NPM), which has over 800,000 development libraries for a variety of uses.
- Learn how to build and manage JSON files in Node.js, which include all of the metadata for the projects you've built.
- Learn the foundations of Node.js, such as variables, data types, operators, and functions
- Learn how to write data to a file instead of the terminal in Node.js by exploring the file system.
- In an event-driven architecture, learn how to build and manage events.
- Learn how to use HTTP modules to create server-side networking applications.
- Experss.js, Meteor.js, AdonisJs, NestJs, Sails, KoaJS, and LoopbackJS are some of the frameworks that are compatible with Node.js.
- Learn how to handle relational databases (SQL Server, PostgreSQL, MySQL), NoSQL databases (MongoDB, Redis), and cloud databases (CosmoDB, DYnamoDB).
- Learn about search engines like ElasticSearch, Solr, and Sphinx.
- Learn how to use Jasmine, Jest, Enzyme, Chai, and other testing tools to do unit, behaviour, and integration testing with Node.js.
Development Skills
Version Control Systems (Git, GitHub):
You don't want to find yourself in a scenario where you've made a mistake in your code and have no idea how to fix it. You can handle huge projects with VCS like Git, and if you're already familiar with VCS, make sure you understand the fundamentals of Version Control Systems.
HTTP/HTTPS protocols:
A basic grasp of how data is transported via transfer protocols can help you become a better Node.js developer, and every backend developer should have a strong understanding of how HTTP and HTTPS function. To secure communications, HTTPS employs the Transport Layer Security (TLS) encryption protocol.
There is a lot to learn in the backend environment, and if you don't know how the web works, it might be a little confusing. There are four request methods that are responsible for any fundamental communication on the web:
GET: To get a representation of a resource, use this method.
POST: To generate fresh resources
PUT: Used to update capabilities
PATCH : Used to modify capabilities
DELETE: To remove a resource indicated by a URL, use this command.
OPTIONS: For a particular URL or server, request an allowed communication option.
Web Frameworks
Express.js: Provides a very basic interface and tools for building our application, is extremely versatile to use, and comes with a number of npm modules that can be inserted right into Express.
Meteor.js: Built-in MongoDB handlers with GraphQL support make this an excellent go-to framework for creating JavaScript apps. When you run the "meteor build myapp" command, an HTML/JavaScript web page with a MongoDB backend is generated.Meteor.js may be an excellent choice in your selection of frameworks for reducing development time and making maintenance easier. Otherwise, if you're making a simple web app, I'd recommend staying with Express.
Sails.js: You can easily create REST APIs, single-page apps, and real-time apps using an MVC framework. If you want to learn some serious skills, Sails.js is a great choice since it offers numerous advantages, like real-time support for WebSockets and a “convention over configuration” approach.
Koa.js: Koa.js is a fantastic choice if you want to develop reliable, future-proof, and easy-to-maintain apps. A Koa application is an object that contains an array of middleware functions that are then stacked and performed.
Nest.js: It's inspired by Angular and written using TypeScript, but it's powered by Express.js, making it compatible with most Express middleware. Nest.js provides a fantastic modular structure for arranging code into distinct modules, allowing you to create an efficient and scalable application.
Database Management
You'll be working with a lot of backed things when learning Node.js, so if you're a newbie, stick to MySQL or SQL at first. Going beyond SQL or MySQL is case dependent when you deal with new sorts of projects and there's a chance you'll need to learn other backend stuff, as you'll receive a clear and straightforward explanation of how we construct backend systems.
SQL Server: Microsoft's relational database management system that supports ANSI SQL (a standard SQL language). SQL, on the other hand, has its own implementations.
MySQL: Another excellent database management solution for creating relational databases. Oracle's open-source backend software; we also have the flexibility of choice with MySQL because we can alter the source code to meet our demands. In comparison to Oracle Database and Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL is a more simple option.
PostgreSQL: It is open source, it was created by a global team of developers. It operates on Linux, UNIX, and Windows, among other operating systems. Complex SQL queries, Foreign Keys, Triggers, Transactions, Multiversion concurrency control (MVCC), Streaming Repllicartons, and other excellent features are all supported by PostgreSQL.
MariaDB: An enhanced version of MySQL that includes a number of sophisticated capabilities, security, and performance enhancements not found in MySQL. For large-scale projects, there are numerous reasons to choose MariaDB rather than MySQL. MariaDB, for example, has a bigger connection pool that can accommodate up to 200,000+ connections, whereas MySQL has a smaller pool. MariaDB is, in a nutshell, quicker than MySQL.
Cloud Database Services
Azure CosmosDB:
A worldwide distributed database service that allows you to manage your data remotely. Using cloud databases has numerous advantages, such as making scaling and managing large applications easier using the tools that Microsoft Azure provides for scaling and distribution.
It also supports different data models with a single backend, making it suitable for document, key-value, relational, and graph models. It's a NoSQL database since it doesn't rely on any schemas, although it does support query language and ACID transactions.
Amazon DynamoDB:
If you already have some SQL expertise, Amazon DynamoDB is a wonderful choice. It is a fully managed NoSQL database service that provides quicker and predictable performance with incredible scalability. You can design database tables that can store and retrieve any amount of data and handle any amount of traffic.
NoSQL Databases
MongoDB: MongoDB is a document-oriented NoSQL database designed for high-volume data storage. Whereas conventional relational databases employ tables and rows, MongoDB utilises collections and documents.
A document in MongoDB is made up of key-value pairs, which are the fundamental unit of data, while a collection is made up of sets of documents and functions, which are the equivalent of tables in relational databases.
Redis: We can deal with databases, caching, and message brokering with Redis. It stores data in the form of key-value pairs using data structures such as strings, hashes, lists, sets, bitmaps, hyperloglogs, and geographical indexes. Here's an example of where we utilise Redix if you're still unsure.
Apache Cassandra
A distributed database that is highly scalable, high-performance, and intended to manage a huge quantity of data across several servers with no single point of failure. It differs from other relational database management systems in that it was developed at Facebook. The data model is built on Google's BigTable, while the distributed architecture is based on Amazon's DynamoDB.
LiteDB
A serverless document storage with a highly lightweight and fast.NET NoSQL integrated database. LiteDB may be used in tiny desktop and online apps that employ a single database per account store for each user.
Search Engines
ElasticSearch
A Java-based search and analytics engine based on Apache Lucene. ElasticSearch allows you to store and analyse large amounts of data in real time.
ElasticSearch has excellent search performance because it searches the index rather than the text. It stores and searches data using structure-based documents rather than tables and schemas that come with comprehensive REST APIs. ElasticSearch may be thought of as a server that handles JSON queries and returns JSON data.
Solr
Field search, boolean queries, phase questions, fuzzy queries, spell check, auto-complete, and many more sophisticated real-time searching features are available.
Caching
Caching is the practise of keeping copies of files in cache memory so that they may be accessed quickly via the network, minimising network calls.
Memory Cache
Caching is frequently connected with memory in servers, this approach is also known as caching. A part of the server's memory is utilised as a cache in this method, where we store all of the data necessary to decrease network calls in our applications. Node-cache and memory-cache are two excellent packages for managing memory cache in a Node server in Node.js.
Distributed Cache
We aggregate the memory of several networks into a single memory data store in this caching approach, which we then utilise as the ultimate data cache to provide rapid access to the data.
This approach is particularly useful when there is a lot of data and a lot of network requests at the same time since it allows for gradual expansion and scalability by adding more server RAM to the cluster. When it comes to distributed caching, Redis is one of the most well-known options, but Memcached can take you much farther.

Template Engines
We may use static template files in our application by using template engines, which during runtime update the variables in a template file with actual values and then turn the template into an HTML file that is given to the client. Some of the most common template engines are listed below.
- Mustache.js
- Handlebars
- EJS
Real-Time Communication
Socket.io
If you're just getting started as a backend developer, there's a lot to learn about real-time communication in Socket.IO. The core logic underlying real-time communication is shared by the client and the server.
It enables bi-directional data flow between the client and the server; you can think of bi-directional data flow as the synchronous flow of data between two terminals to achieve real-time communication behaviour; these types of behaviour are enabled when the client has Socket.IO installed in the browser and the server has the Socket.IO package installed. And the information may be supplied as JSON requests.
API Clients
REST
APIs were formerly built around a remote procedure call (RPC), and the APIs seemed to be locally run code. Many systems attempted to tackle this problem by utilising RPC-like stacks to obscure the fundamental problem, and then REST was developed to improve the development of web-based APIs.
Under the REST design, simple HTTP requests are utilised to interact rather than more sophisticated options like COBRA, COM+, or RPC. RESTful calls are made using messages that are specified using HTTP standards. In the Node.js environment, you may pick between node-rest-client and Axios, both of which provide outstanding speed for web applications.
GraphQL
GraphQL is a fantastic alternative to REST since it makes use of APIs that prioritise providing clients with exactly the data they need. It's a developer-friendly option since it can be used in an IDE called GraphiQL. You may also add or remove fields without affecting current searches, and construct APIs using whichever technique you want.
Node.js is a well-known back-end JavaScript framework that continues to be popular among software developers and enterprises. It will not be difficult to discover a Node.js development firm with highly qualified experts willing to offer their technical skills if you are seeking for Node.js developers.
Node.js is used by software developers because it can handle a large number of simultaneous requests, has excellent app scalability, and is simple to install and use. To become full-stack engineers, many front-end developers learn Node.js.
This framework is used by businesses because it enables the development of robust, cross-platform, and real-time applications. Companies may use this method to integrate streaming and instant-messaging capabilities into their apps, making them more engaging and effective. Hope this node js developer roadmap blog would have enlightened you on becoming a node js developer.
FAQs
1. How do I learn node JS roadmap?
- Learn JavaScript.
- Understand why It Is Called Node.
- Understand non-blocking in Node.
- Learn the Concept of the Event Loop.
- Learn the Global Variables.
- Learn How to Use the Libraries That Come With Node.
- Learn Code Writing for Node.
- Without Using Any Frameworks, Write a Web Application on Node.
2. Is node js worth learning 2023?
Many experts say whether is node js worth learning 2023 or not depends on your preferences. However, before you answer, you must know that Node js popularity in 2023 is expected to grow even more.
3. Does node js have a future?
When it comes to servers that do numerical computations and machine learning, Python is the superior choice, whereas Node js shines in most sorts of web services, especially real-time apps. Unlike Python, NJS enables asynchronous programming by default, allowing for greater scalability and performance.
4. Is node js developer in demand?
Developers adore Node. js because it is open source and free in addition to everything else, particularly JavaScript developers who wish to advance their coding skills. Node. js engineers are in great demand because employers are interested in the quicker, real-time, event-driven servers of today.
5. node js developer salary
The average yearly income for a Node JS Developer in India is 5.0 Lakhs, with salaries ranging from 1.9 Lakhs to 12.0 Lakhs. In the USA, the typical node js developer makes $120,000 a year, or $61.54 an hour. Most experienced professionals earn up to $149,731 year, while entry-level occupations start at $100,063 annually.
6. How to become node js developer
One should go through the following steps to become a node js developer
- Discover the basics of JavaScript programming. Learn about the inner workings and fundamentals of Node.js.
- Proficient with Node.js APIs. Learn how to construct a practical Node.js application.
- Find out how to stop unauthorized users from accessing protected web sites.

Accelerate Your Career with Crampete




